Contents
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the key distinctions between ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) systems!
In the ever-evolving landscape of fashion business technology, understanding the unique roles and functionalities of these two essential software solutions is paramount.
Whether you're a seasoned professional or new to the world of fashion enterprise software, this introductory exploration will shed light on the fundamental differences between ERP and PLM, empowering you to make informed decisions for your organization's needs.
Let's dive in!
What are the Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems?
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are software solutions designed to streamline and integrate core business processes and functions across various departments within an organization.
ERP systems tailored specifically for the fashion industry offer specialized features to address the unique needs and challenges of fashion businesses.
These ERP solutions typically include modules and functionalities such as:

- Product Lifecycle Management (PLM): Integrated PLM capabilities enable fashion companies to manage the entire lifecycle of their products, from concept and design to production and distribution.
- Style and SKU Management: Fashion ERP systems provide tools for managing styles, variants, sizes, colors, and other product attributes efficiently.
- Seasonal Planning and Merchandising: They support seasonal planning, assortment planning, range management, and merchandising to optimize product offerings and align with market trends.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM): SCM modules help fashion businesses streamline sourcing, procurement, vendor management, and logistics to ensure timely delivery and optimal inventory levels.
- Inventory Optimization: Fashion ERP systems offer advanced inventory management capabilities, including demand forecasting, stock allocation, replenishment planning, and multi-channel inventory synchronization.
- Omni-channel Retailing: They support seamless integration across various sales channels, including e-commerce platforms, brick-and-mortar stores, wholesale, and mobile apps.
- Production Planning and Control: These systems assist in capacity planning, production scheduling, work order management, and quality control to optimize manufacturing processes.
- Compliance and Regulatory Requirements: Fashion ERP solutions help businesses comply with industry-specific regulations, sustainability standards, and product safety requirements.
- Financial Management: They include accounting, budgeting, cost management, and financial reporting functionalities tailored to the needs of fashion companies.
- Business Intelligence and Analytics: Fashion ERP systems provide tools for real-time reporting, dashboards, and analytics to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) and gain actionable insights into business operations.
Leading ERP vendors offering solutions for the fashion industry include Aptean, CGS BlueCherry, Infor Fashion, RLM Apparel Software, and Visual Next, among others. These systems help fashion businesses streamline operations, improve visibility, and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving market.
What are Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) systems?
In the fashion industry, Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) systems are specialized software solutions tailored to the unique needs and processes of fashion businesses.
These PLM systems offer features and functionalities specifically designed to manage the entire lifecycle of fashion products, from initial concept to final production and beyond.
Key components of PLM systems in fashion include:

- Design and Development: PLM systems facilitate the design and development process by providing tools for sketching, creating digital prototypes, managing color and material libraries, and collaborating with designers and creative teams.
- Material and Trim Management: Fashion PLM platforms help manage materials, trims, and components used in product development, including sourcing, tracking, and organizing information related to fabrics, embellishments, and accessories.
- Style and SKU Management: PLM systems enable fashion companies to manage styles, variants, sizes, colors, and other product attributes efficiently, ensuring consistency and accuracy across product lines.
- Sample Management: These systems streamline sample management processes, from sample requests and approvals to tracking and shipping samples to vendors, buyers, and stakeholders.
- Tech Pack Creation: Fashion PLM solutions facilitate the creation and management of technical packages (tech packs) containing detailed product specifications, measurements, construction details, and other critical information needed for production.
- Fit and Sizing: PLM platforms include tools for managing fit sessions, capturing feedback, and iterating on product designs to ensure optimal fit and sizing across different body types and markets.
- Supply Chain Collaboration: Fashion PLM systems enable collaboration with suppliers, manufacturers, and vendors throughout the supply chain, facilitating communication, sourcing, procurement, and production planning.
- Quality Assurance and Control: These systems support quality management processes, including quality inspections, defect tracking, and resolution, to ensure products meet quality standards and customer expectations.
- Regulatory Compliance: Fashion PLM solutions help companies comply with industry regulations, sustainability standards, and product safety requirements, ensuring products meet legal and ethical standards.
- Line Planning and Merchandising: PLM platforms assist in seasonal planning, range management, assortment planning, and merchandising strategies, helping fashion companies optimize product offerings and align with market trends.
Fashion PLM systems play a critical role in streamlining product development processes, improving collaboration, reducing time-to-market, and enhancing overall efficiency and competitiveness in the fast-paced world of fashion. Leading vendors offering PLM solutions for the fashion industry include Techpacker, Centric Software, Lectra, YuniquePLM by Gerber Technology, and PTC FlexPLM, among others.
What is the difference between ERP and PLM systems?
In the realm of fashion, Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) systems serve distinct yet complementary purposes:
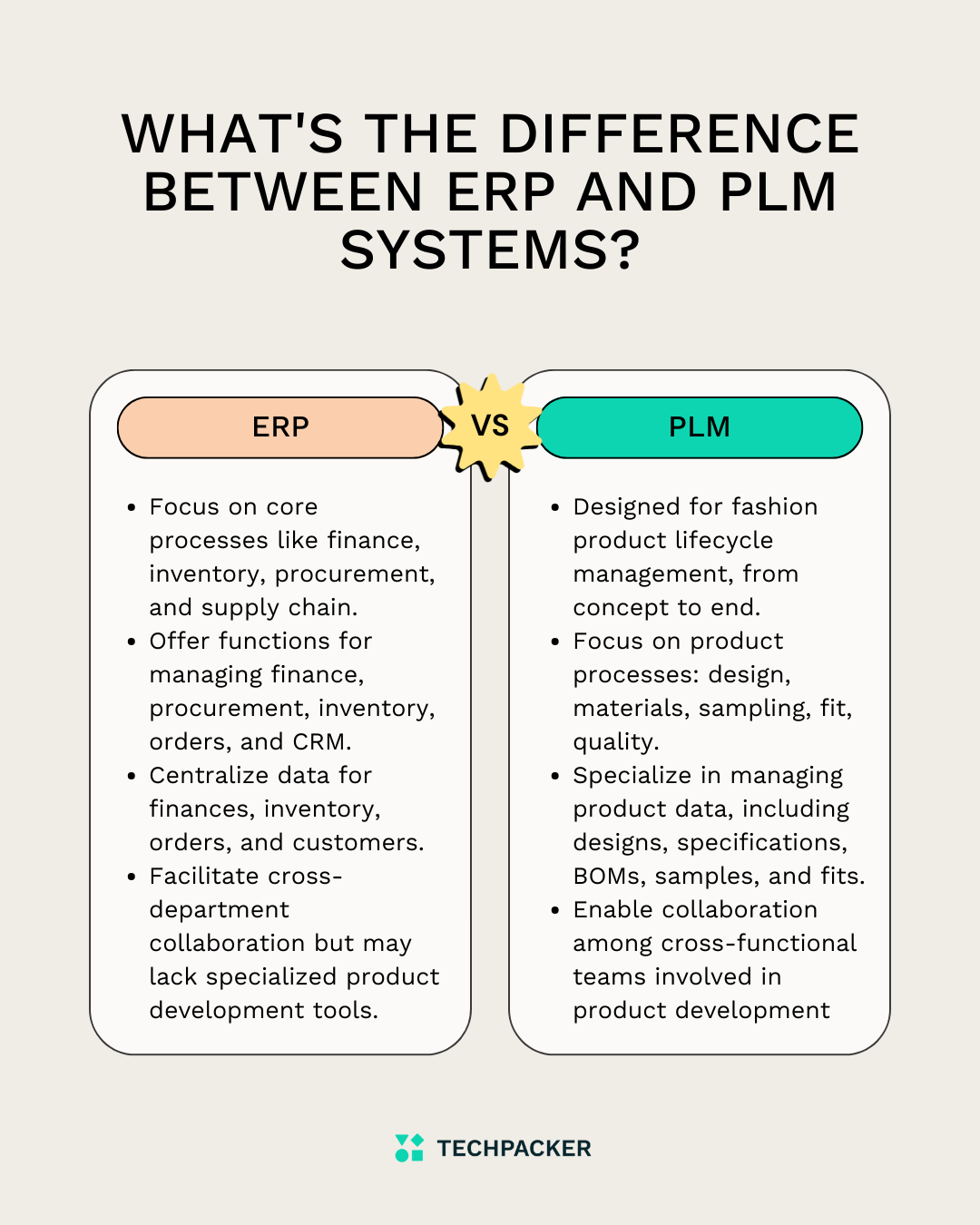
Scope and Focus:
- ERP Systems: Primarily focus on managing core business processes such as finance, inventory, procurement, and supply chain across the entire organization. In fashion, ERP systems handle functions like accounting, inventory management, order processing, and supply chain logistics.
- PLM Systems: Specifically designed to manage the lifecycle of fashion products, from concept to end-of-life. PLM systems in fashion are tailored to handle tasks related to design, product development, sourcing, production, and merchandising.
Functionality:
- ERP Systems: Offer functionalities for managing financial transactions, procurement, inventory, order fulfillment, and customer relationship management (CRM). They provide a broad overview of business operations.
- PLM Systems: Focus on product-related processes such as design collaboration, material management, sample development, fit analysis, and quality control. PLM systems offer detailed insights and tools for managing the complexities of product development in fashion.
Data Management:
- ERP Systems: Centralize data related to financial transactions, inventory levels, sales orders, and customer information. While they may handle some product-related data, it's usually not as detailed or specialized as PLM systems.
- PLM Systems: Specialize in managing extensive product data, including designs, specifications, bills of materials (BOMs), sample details, and fit specifications. PLM systems ensure accuracy and consistency in product information throughout the development process.
Collaboration:
- ERP Systems: Facilitate collaboration across different departments such as finance, sales, and procurement but may lack specialized tools for collaboration in product development.
- PLM Systems: Enable collaboration among cross-functional teams involved in product development, including designers, product developers, suppliers, and manufacturers. PLM systems streamline communication and decision-making throughout the product lifecycle.
In summary, while ERP systems provide a broad framework for managing business operations, PLM systems offer specialized functionalities for managing the intricacies of product development in the fashion industry.
Both systems play crucial roles in optimizing efficiency, reducing costs, and enhancing competitiveness, but they serve different aspects of the fashion business. Integrating ERP and PLM systems can provide a comprehensive solution for managing both business processes and product development in fashion companies.
Which system is right for your business?
Fashion brands can determine whether they need to adopt an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) or Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) system by considering the following factors:
Business Needs and Objectives:
- Assess the specific goals and priorities of the fashion brand. If the primary focus is on optimizing core business processes such as finance, inventory management, and supply chain logistics, an ERP system may be more suitable.
- If the main objective is to streamline product development, enhance collaboration among design and development teams, and manage the entire lifecycle of fashion products, a PLM system would be more appropriate.
Current Pain Points and Challenges:
- Identify the key pain points and challenges faced by the fashion brand in its operations. If issues revolve around inventory management, order processing, and financial management, an ERP system may address these concerns effectively.
- If challenges are related to product development inefficiencies, lack of visibility into the design process, or difficulty in managing product data and specifications, a PLM system could offer solutions to these issues.
Size and Complexity of Operations:
- Consider the size and complexity of the fashion brand's operations. ERP systems are often favored by larger companies with complex supply chains and extensive business processes.
- PLM systems are particularly beneficial for fashion brands that deal with a high volume of product development activities, collaborate with multiple suppliers and partners, and manage diverse product lines.
Stage of Growth and Expansion Plans:
- Evaluate the stage of growth of the fashion brand and its expansion plans. If the brand is in a rapid growth phase or planning to expand into new markets, an ERP system can provide scalability and support for business expansion.
- For brands looking to innovate their product offerings, launch new collections, or improve time-to-market, a PLM system can enable faster and more efficient product development processes.
Budget and Resources:
- Consider the available budget and resources for implementing and maintaining an ERP or PLM system. ERP systems often require significant upfront investment in software licenses, implementation, and training.
- PLM systems may also involve substantial costs, but they can offer a higher return on investment by improving product development efficiency and reducing time-to-market.
Ultimately, fashion brands should carefully assess their unique requirements, priorities, and long-term objectives to determine whether an ERP or PLM system is the right fit for their business. In some cases, integrating both systems can provide a comprehensive solution to address both business process optimization and product development needs. Consulting with industry experts and conducting thorough evaluations of available solutions can help fashion brands make informed decisions regarding system adoption.


