Contents
When we talk about garment manufacturing we usually think about cutting, sewing and finishing processes. However, garment manufacturing is not complete without the pre-production processes. In this post we will explain what pre-production processes mean, what steps they include and discuss the types of samples made prior to bulk manufacturing.
What pre-production processes mean
Pre-production process is planning that is done prior to the bulk garment production. That includes samples development and approvals, sourcing and testing raw materials, garment costing, pattern making, and process planning. Efficient production can’t be reached without the pre-production processes.
In garment manufacturing a typical pre-production process is divided into five steps:

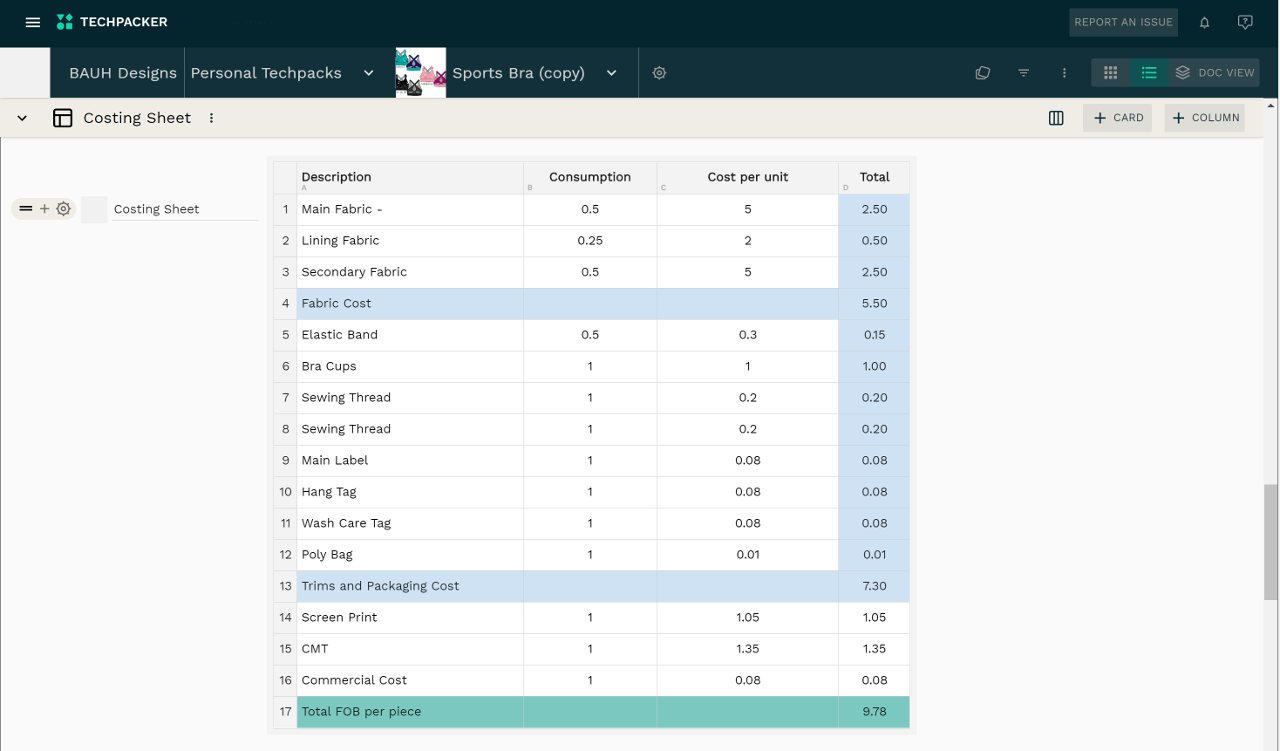
Costing of a garment
Costing of a garment is a process of calculating and combining raw material costs, trims, packaging, labor, shipping, and operating expenses. In general, it estimates and determines the cost of producing a piece of clothing.
Costing is a very critical stage. If the cost is low there will be no profit, if the cost is too high it will be harder to sell the product.
Pattern making, grading
Pattern making is the process of creating a blueprint of a garment. When constructing a piece of clothing the fabric is cut according to the pattern instructions and specifications. The main purpose of a pattern is to make 2D fabric sit properly on a 3D body. Therefore it is created with the type of fabric and trims in mind, and the intended fit.
Follow our guide on apparel pattern making for fashion designers.
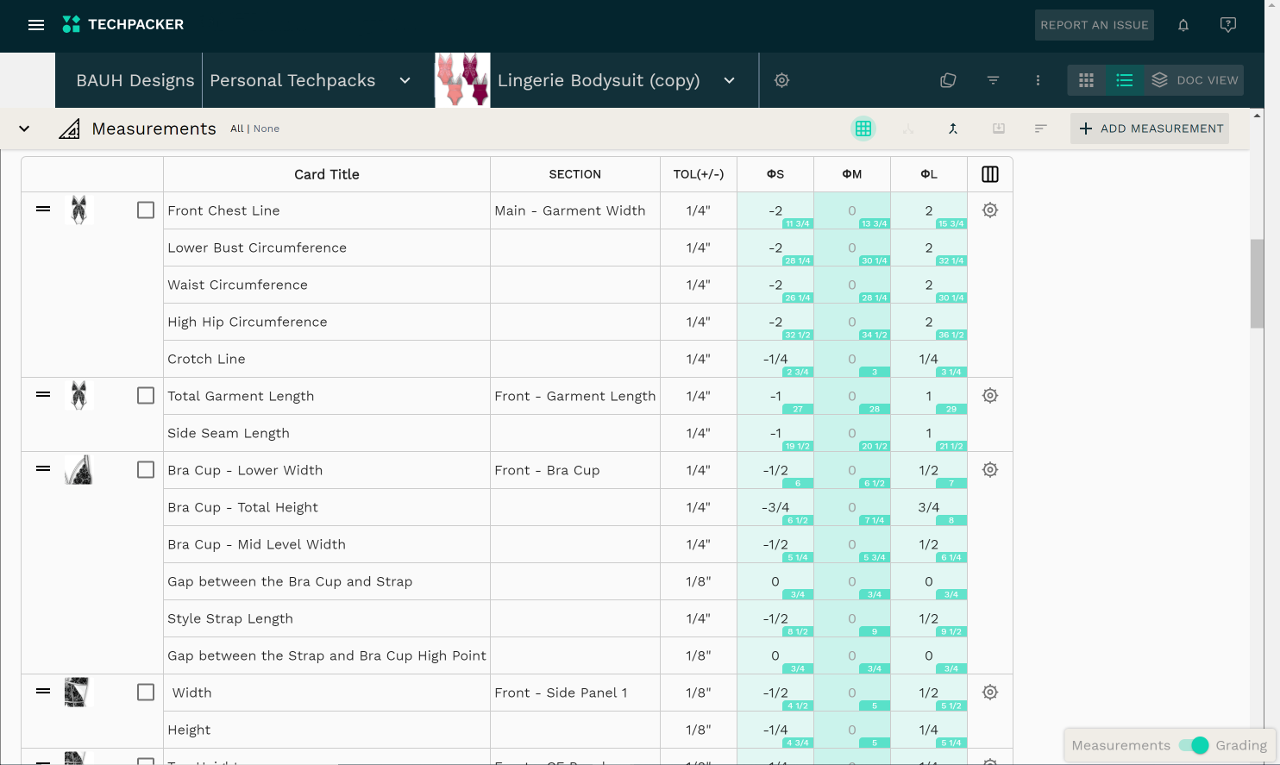
Pattern is usually created by a technical designer or a professional pattern maker. They develop a first fit pattern and then can re-develop it adding comments and rectification on a fit sample. After fit approval pattern maker does the grading for size set samples only for the specified sizes. The pattern is graded for the whole size range once everything is approved and the order is ready for production.
New technologies like Techpacker allow you to do grading automatically based on your measurements. Instead of creating the grading sheet separately here you can view your measurements and grading in one place. Here is how it works:
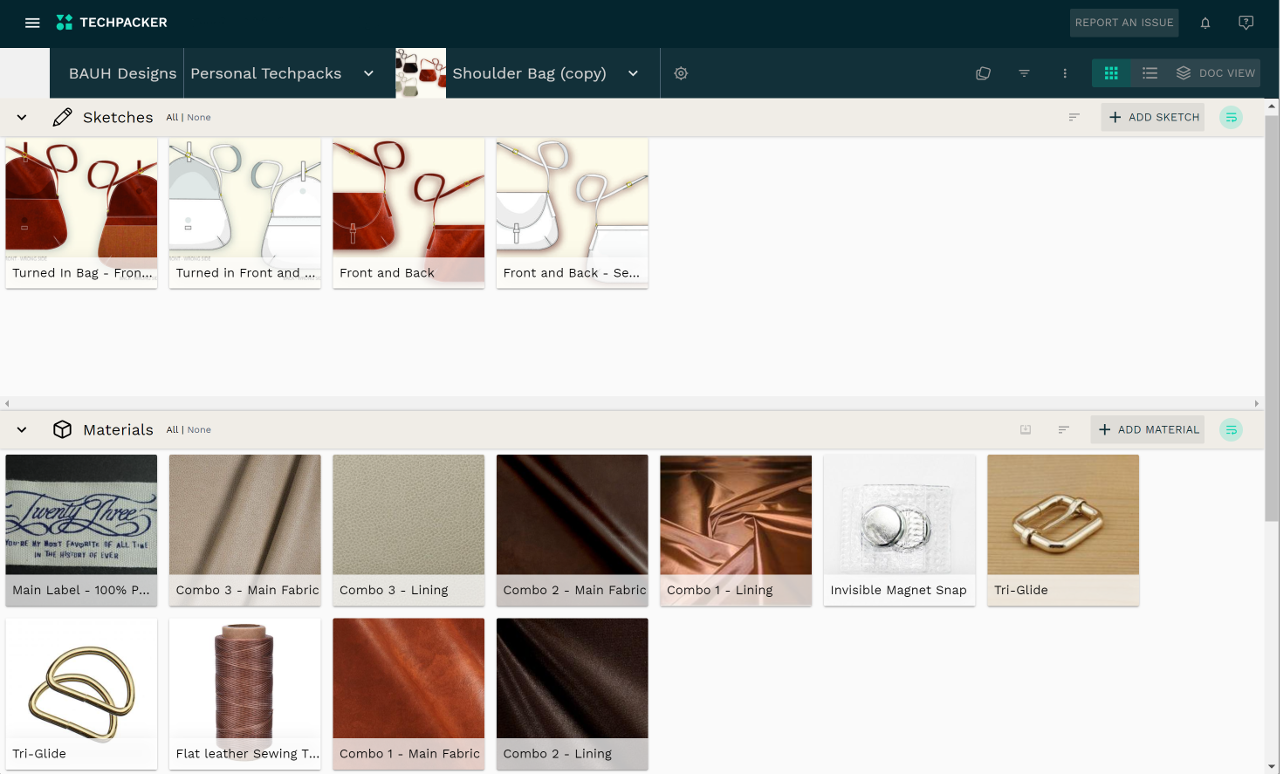
Sourcing raw materials
Sourcing raw materials includes fabric selection and finding a sourcing company to work with. These materials include fabric and all kinds of trims and accessories. All of these elements go into the Bill of Materials in the Tech Pack.
Bill of Materials (BOM) is a complete list of all items with corresponding costs and quantities that are required to build a product whether it’s a piece of clothing, shoes, or accessories. The main purpose of BOM is to estimate raw materials costs, plan purchases and reduce the amount of waste. It also helps you never miss a single thread, button, zipper, or tiny detail when manufacturing your products.
After the materials are selected and sourced, physical properties are being tested for bulk manufacturing. This test can be done with the help of a manufacturer or in in-house testing labs.
Process planning
After the raw materials are sourced, a pattern is approved and the cost of a garment is calculated, the company starts to plan the process with the factory. They plan when to start cutting when to submit the pre-production sample when to sew and finish the final garments. At this point, the time period of the final inspection and quality check is estimated and the shipment date is set.
Pre-production sample and quality check
The pre-production sample (PPS) is a sample of the product that is made before manufacturing starts. It helps buyers examine the design, materials, labeling and construction details like stitching.
At this stage, the buyer can request changes if needed. However, depending on the supplier agreement, additional costs may occur. Which may be well worth it in order to ensure the best outcome.
Once the PPS sample has been approved the large-scale production can begin.
Why pre-production samples are important
Pre-production samples are important because they ensure that they match the original quality and standards of the product created during the development process. It helps the company requesting the PPS sample evaluate the factory's manufacturing skills and the ability to meet the quality requirements.
The other primary purpose of the pre-production sample is to define any problems with the product during the early stages. And make corrections before bulk production begins. PPS also helps the company calculate the actual cost of production and production time.
How is PPS different from other types of samples
Apart from the pre-production sample, there are other kinds of samples commonly used in the clothing manufacturing industry.
The PPS sample is the first critical step before bulk production. It can also be used for pre-selling and marketing purposes. After the PPS sample is approved, it becomes a Production sample.
Production sample then goes into a limited production run, sometimes limited to a single size or color way. At this stage, the manufacturer can perform a size run to verify that final products are consistent with size standards.
After the successful limited run of the production sample, the products are inspected to ensure quality. The formal start of production starts with the Top Production sample. At this stage, the Quality Control inspector of the company visits the manufacturer to check out the production line and pick a garment for evaluation. If the production is made in-house the same process applies - samples are inspected and the quality check is performed.
For marketing and presentation to potential buyers, the Sales sample is used. The Sales sample represents the actual product. This type of sample allows vendors to determine the marketability of the product. After approving the concept subtle changes can be made to fabric combinations, colorways, or trims. However, any of those changes cannot affect the production process.
In total there are 12 types of garment samples that you should know.
Fit sheets
After the company receives the first fit sample from the manufacturer they make sure the desired fit is achieved. And that the sample corresponds to the necessary measurements and specifications. To evaluate the sample and suggest any revisions the Fit table is created.
Here is an example of a Fit table. Techpacker lets you generate a Fit Sheet in one click. It extracts measurement specs from your Measurement table.
As you enter your sample specs in the FIT column, the table monitors them with your provided tolerance range, and if any differences are found it instantly highlights them for you.
Study of the approved sample
The study of approved samples helps find the best way to produce the garment. At this stage, companies can define the most efficient way to manufacture their product.
Once the sample is approved and the materials are sourced the production planning department conducts a pre-production meeting. Over the meeting production team, quality team, and sourcing team share their comments and discuss dos and don’ts. They also schedule the planned cut date, shipment date, and a purchase order is placed with the clothing manufacturer for bulk production. The contract has to be very detailed and includes delivery dates, fabrics, trims prices. It binds both the brand and the factory and ensures that each party fulfills its obligations. Before the bulk production begins all samples should be approved and meet the requirements and details like labels, size sets, tags, packaging, etc.
|
Manage your entire pre-production processes from one place OR |



