Contents
Dive into the world of clothing manufacturing! In this blog post, we will discuss how the clothing manufacturing business works, how to start your own apparel production business and how to collaborate with brands (including the legal aspect of it).
Let's start with the basics.
What is clothing manufacturing?
Clothing manufacturing includes numerous operations necessary to make a garment. It includes processes like cutting, sewing and finishing. The whole manufacturing process breaks down into a number of sub-operations needed for constructing a particular garment. Some of these operations vary depending on the type of equipment available, work methods used and workers’ skills.
How clothing manufacturing business works
Clothing manufacturing is a complex process that includes multiple steps. We defined the five most important stages.
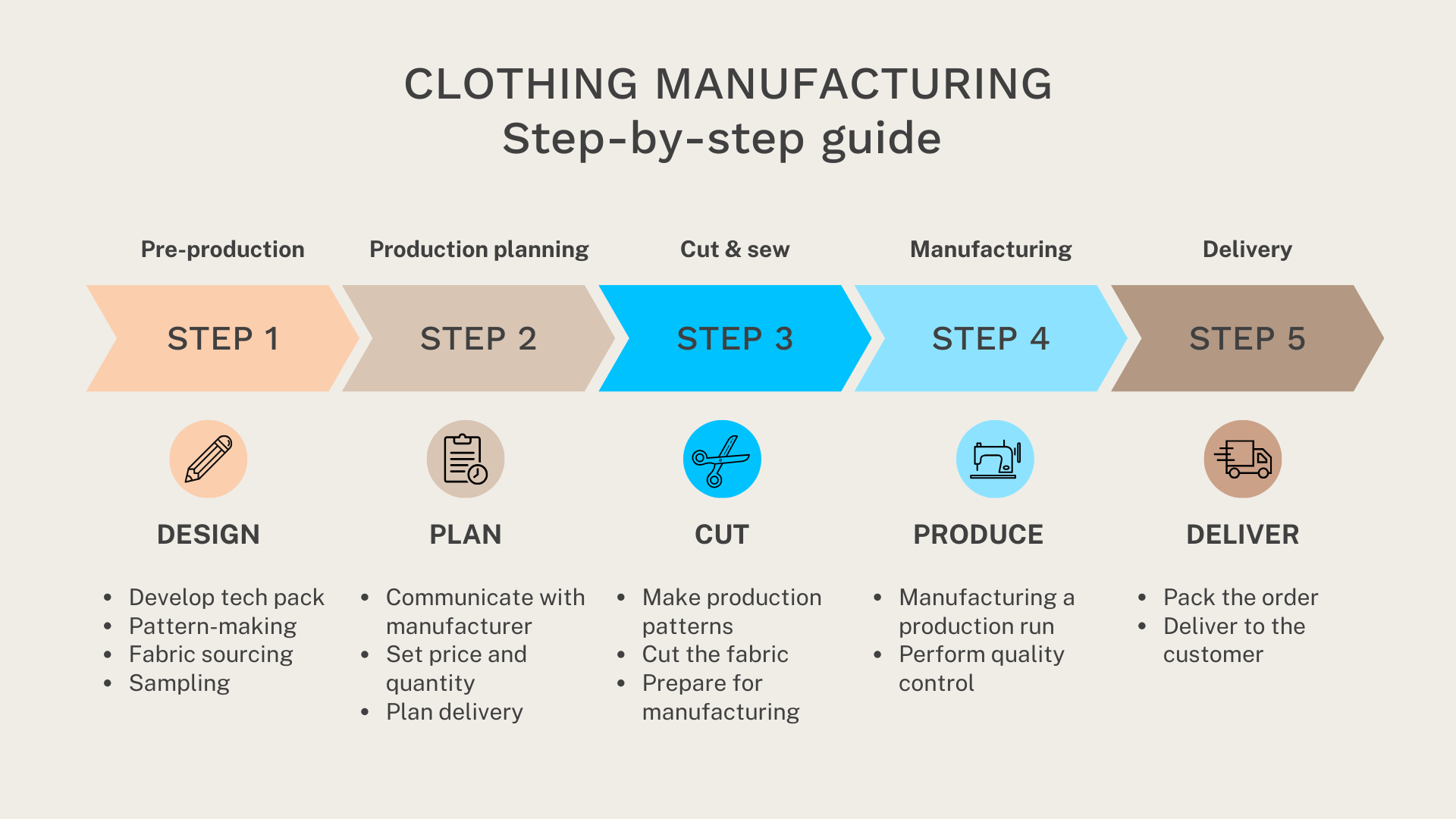
Clothing manufacturing consists of the following steps:
- Pre-production. Including materials sourcing, pattern making, and sampling.
- Production planning. The planning team foresees the production and makes sure all activities are completed on time.
- Cutting process. Using the guidelines provided by the designer, the factory cuts the fabric for sewing. Modern garment manufacturers use laser-cutting technology to prevent wastage.
- Manufacturing and quality control. Once the production is complete the factory will perform quality the quality check. The customer has a right to reject items if they don’t meet the expected standards and quality.
- Delivery. After the garments pass the quality control, the rest of the production order will be delivered to the customer.
Pre-production processes in garment manufacturing
The pre-production process is planning that is done prior to the bulk garment production. That includes samples development and approvals, sourcing and testing raw materials, garment costing, pattern making, and process planning. Efficient production can’t be reached without the pre-production processes.

In garment manufacturing a typical pre-production process is divided into five steps:
- Calculating the cost of a garment.
- Pattern making and grading.
- Sourcing raw materials.
- Production process planning.
- Creating a pre-production sample.
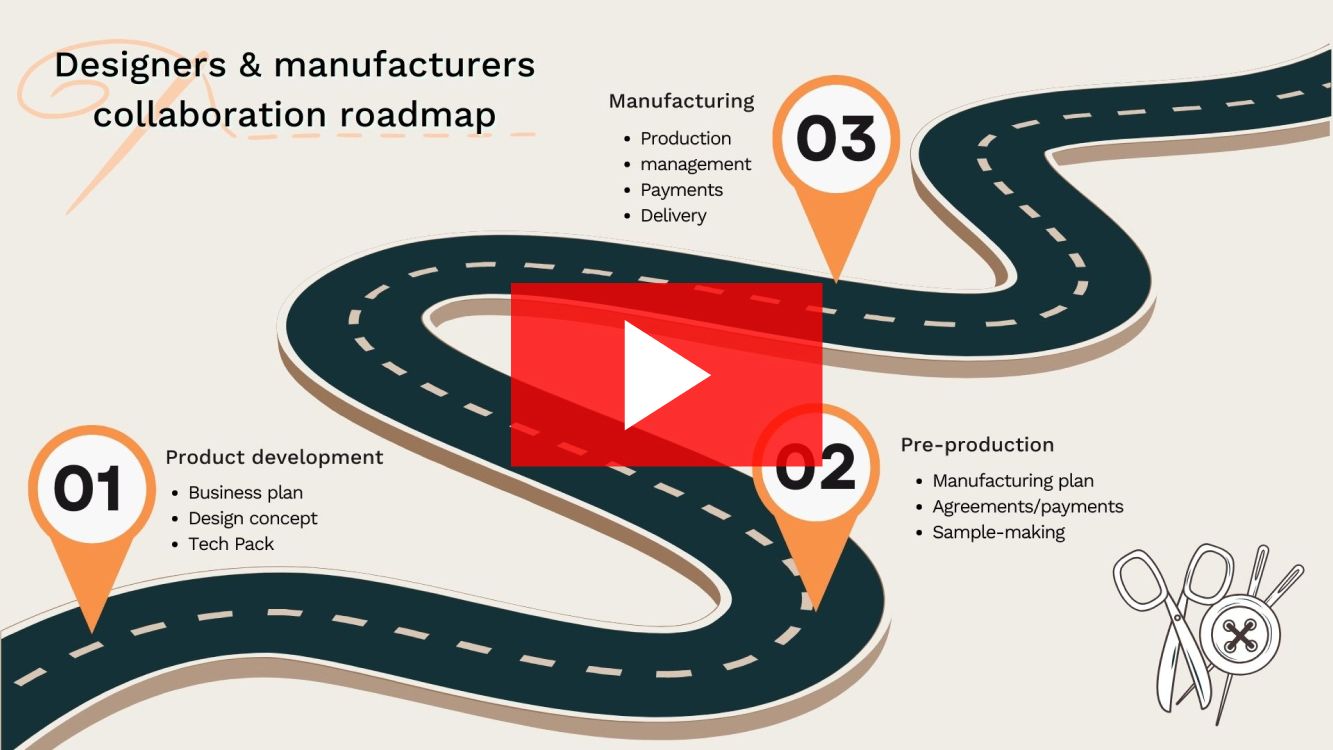
How designers and clothing manufacturers collaborate on clothing lines
Collaboration between designers and manufacturers is the foundation of the apparel business. The first time you communicate with each other you need to have clear expectations of what result you want and how each side will operate together.
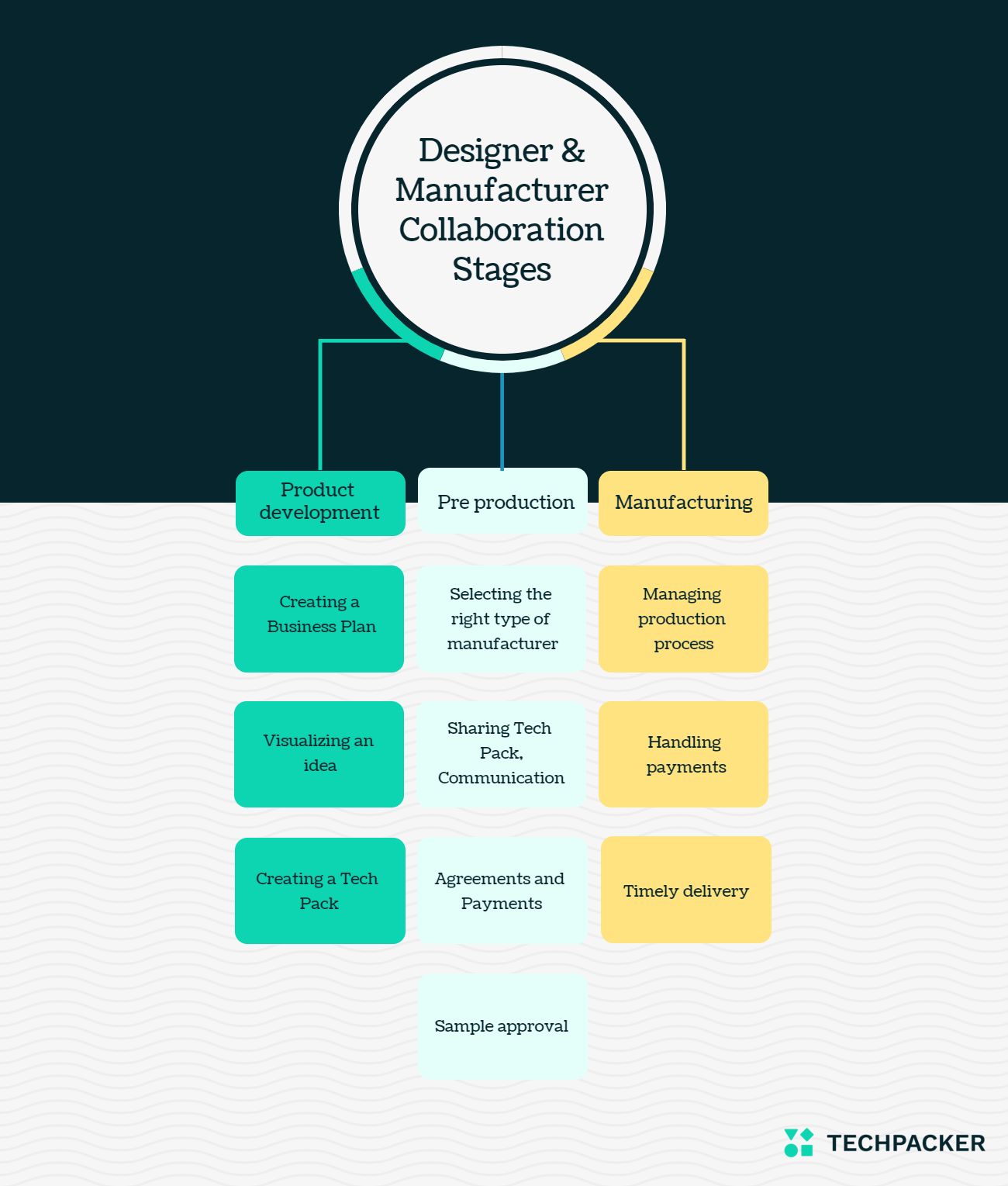
The process of collaboration between designer and clothing manufacturer can be broken down into three stages:
- Product development. At this stage, the designer creates a business plan, visualizes an idea, and develops a Tech Pack.
- Pre-production. This stage includes finding a manufacturer to work with, making a production agreement, and creating a sample.
- Manufacturing. Managing the production process includes precise planning of the on-time shipments, effective use of labor, and overseeing the needed supplies and equipment for each order.
How to request a price quotation from garment manufacturers
When the clothing designer comes up with a new collection, they need to get an estimate of how much it is going to cost to produce it. Tech pack in hand, and with a list of potential suppliers, now they need to request pricing quotations to see which factory can work with their budget and timings, while still meeting the quality needs.
Follow this price quotation strategy to get accurate quotes from suppliers. This way designers can make the right decision when it’s time to produce their collection.
Sign up for our FREE membership and get access to
All premium articles
E-courses and ebooks
Ad-free experience
Tech pack templates
12 types of garment samples you should know about for apparel production
Even though, in essence, apparel production is not a very complicated process, there are stages we need to see through carefully before garments can be sent out for production successfully. Each and every one of these steps comes with a fair share of sample making, testing, and adjusting.

There are several ways to go about garment sampling and it’s important to know and understand the different kinds that exist to see which ones work best for your production needs.
In total there are 12 types of garment samples:
- Mock-up sample.
- Photo or development sample.
- Digital garment sample.
- Fit sample.
- Size set sample.
- Salesman sample.
- GPT sample.
- Pre-production sample.
- Sealed sample.
- TOP sample.
- Shipment sample.
- Press sample.
Production planning and cutting
During the production planning stage, the planning team foresees the manufacturing and makes sure all activities are completed on time. Depending on the type of manufacturer the production planning and cutting may vary.
Let's talk about the main types of garment manufacturers.
Clothing manufacturers and their types
There are various types of clothing manufacturers depending on the type of services they provide. The main ones are:
- CMT (Cut, make, trim) clothing manufacturers. They provide a service that includes cutting, trimming, and sewing the garment into a fully finished product.
- FPP (Full Production Package) clothing production. It is a clothing production type where a manufacturer provides all stages of garment building to the brand.
There are also low minimum clothing manufacturers and mass production clothing manufacturers. New clothing businesses that are ready to start manufacturing their clothing are usually looking for MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity) clothing manufacturers. Mass production clothing manufacturers are those behind department stores and world-known brands.
Manufacturing and quality control
Once the design is approved and the tech pack is complete, the brand is ready to start the production order. At this stage, designers have to make decisions about quantities, size, and color breakdowns. This is in addition to getting a quote and estimated shipping date for their order.
What is a purchase order sheet?
To document the production agreement in garment manufacturing, a Purchase Order Sheet is used.
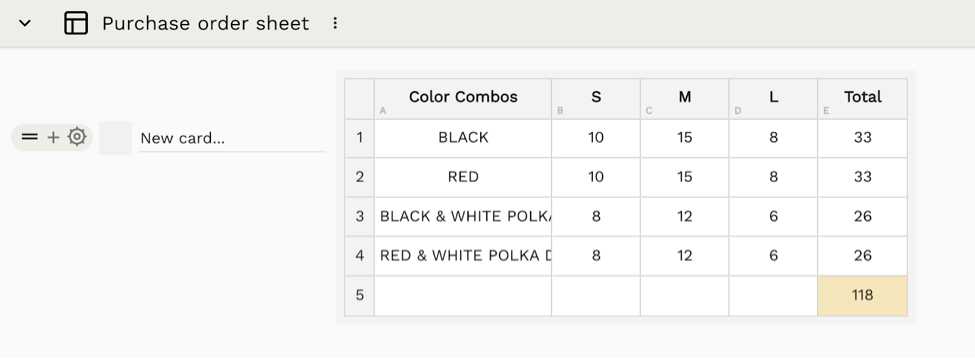
In general, the PO sheet includes all necessary information on a specific order lot and is followed by the merchandiser from raw materials booking to packing and preparing for export.
Garment quality assurance & quality control
Quality in garment manufacturing is a very broad subject as it encompasses both process and product as you will learn later. But it basically constitutes the characteristics of a salable good that determine its desirability and which can be controlled by a manufacturer to meet certain basic requirements.
Most businesses that produce goods for sale have a product quality or assurance department that monitors outgoing products for consumer acceptability.
Quality assurance and quality control may seem the same thing, but they’re not. Apparel garments, accessories, and other textile products are assessed for quality in the preproduction phase, during production, and with a final inspection after the product has been completed.
Quality Assurance is focused on the process. It builds quality into each step of the manufacturing process including designing, production, and beyond.
Quality Control is focused on the product. It is generally understood as assessing the quality of products upon completing manufacturing and after being classified into acceptable and unacceptable categories where checking of the actual results are done to ensure that things are as expected.
Pre-production sample order terms
Developing pre-production samples is the only way to truly test the viability of a new design, and the manufacturers capability to produce it. It’s also a minefield, that can cost you months, sometimes up to a year, in lost time if not managed properly. The first step of the pre-production sample development is to draft Sample Order Terms. A well drafted document can save you thousands of dollars in development costs, and prevent severe delays caused by never ending sample revisions.
To draft a Sample Order Terms Documents make sure to include the following details:
- Product details like CAD files, Bill of Materials, color codes, size table, etc.
- All applicable product regulations, including technical standards and substance restrictions, must be communicated to the manufacturer before they get started on the samples.
- Product packaging and labelling requirements.
Samples rarely come out perfectly on the first try. Depending on the product and its complexity, two to three revisions are to be expected. However, you don’t want to end up in a situation where the supplier is asking you for more money, because they failed to get your approval on the pre-production samples. For this reason, include the following terms:
- Your planned number of sample revisions.
- Revision cost terms.
- Sample revision time.
- Refund terms in case if the supplier fails to produce sample within the requested time.
- Mold and tooling ownership.
- Payment terms.
- NDA agreement.
For more information about Sample Order Terms visit our complete guide here.
Production delivery
During the garment manufacturing stage, a factory will need to comply with a certain amount of legislation. Designers need to be aware of the local regulations while considering importing or exporting their goods.
Handling the legal part of the clothing manufacturing stage
Some of the most common clothing manufacturing regulations in the US are:
- Registration of chemicals.
- Flammable fabrics regulations.
- Consumer safety regulations that regulate only children’s products for kids under 12 years of age.
- Clothing and textile standards cover textiles that are commonly used for weaving and knitting.
- Clothing labeling rules.
- Fur and Wool Products Labeling Act.
A garment manufacturing agreement can help eliminate many potential problems that may happen between a brand and a manufacturer. It is beneficial for both sides. Whether a company manufactures locally or goes overseas, it’s crucial to put together a manufacturing agreement that protects the brand, factory, and its workers.
Follow our guide on what to include in a garment manufacturing agreement ( + sample agreement).
Textiles labeling requirements
Labeling requirements are mandatory. This cannot be stressed enough. If you import or manufacture apparel without the necessary information and graphics, your product is illegal and cannot be placed on the market.
In general, all labels for products imported into US have to include:
- Country of origin
- ASTM Care Labels
- English Language
- Fiber Composition
Difference b/w FOB and CIF in the apparel industry
When you buy materials or ship your manufactured garments across national boundaries, you and your supplier/factory must have a clear understanding of the Incoterms like CIF and FOB - two of the most commonly used shipping agreements.
The biggest difference between FOB (Free on Board) and CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) agreements is the point at which responsibility and liability of goods transfer from seller to buyer.
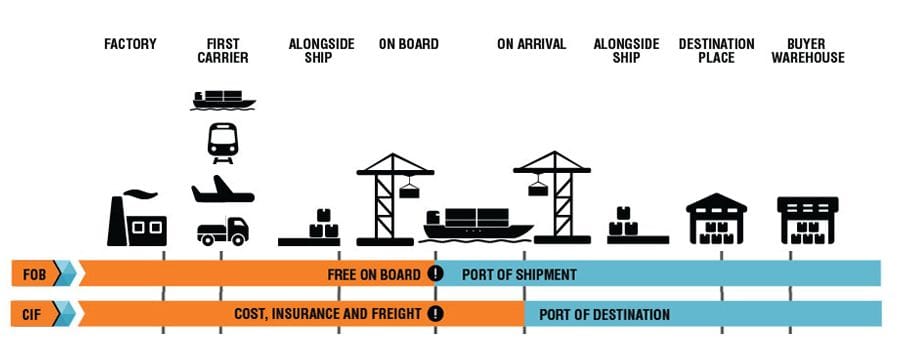
Each agreement has particular advantages and drawbacks for both parties. With FOB shipment, responsibility and liability transfer from the seller to buyer when the shipment reaches the port or other facility designated as the point of origin. With CIF agreement, the seller pays costs and assumes liability until the goods reach the port of destination chosen by the buyer. CIF is considered a more expensive option when buying goods. Very often sellers prefer FOB and buyers prefer CIF.
Sign up for our FREE membership and get access to
All premium articles
E-courses and ebooks
Ad-free experience
Tech pack templates
Top 9 clothing manufacturing trends
The fashion industry needs to evolve quickly to respond to the need of ensuring the right products at the right price, the right time, and the right customers through improved and sophisticated processes. This has required the persistent digitization of manufacturing through increasingly connected devices and platforms.
There are many trends shaping the future of manufacturing, but we’ve identified nine main aspects that have the most influence right now and are generating more components:
- The rise of machine learning. Today, advanced algorithms are transforming the way the manufacturing industry collects information, performs skilled labor, and predicts consumer behavior.
- Supply-chain optimization. As people become increasingly “impatient” shortening lead times is key to ensure delivery with optimum timing.
- Fashion on demand. New technologies like automation and data analytics are shifting consumer needs to just-in-time production.
- Robot designs for the manufacturing floor. The latest advancements have equipped robots with memory and agility making them highly programmable and collaborative.
- Digital factories. These technologies allow companies to produce highly-customized products and gain significant efficiency.
- Rapid data analysis for quick adaptation. Thanks to the Internet and new software brands and factories can receive real-time feedback and alert companies of defects or damaged goods helping them save money and eliminate waste, helping deliver adequate products at the perfect time.
- Manufacturing CRM. It allows manufacturing businesses to get insights into customers' needs that can be used for improving existing products and help develop new ones.
- 3D Design, printing, and mass customization. 3D printing can help them produce goods on-demand and create new avenues for customization.
- Better working conditions. An increasing amount of global fashion brands have been making agreements to work with suppliers, governments, and NGOs to ensure a fair living wage and better working conditions for workers.
Eco-friendly clothing manufacturing
Fast fashion has taken the world by storm. With a promise of providing the trendiest styles by replicating the designs of top fashion brands in a quick and affordable manner, it seems too good to be true. Oftentimes, these clothes are produced quickly with short-lasting fabrics, hence why it’s called “fast” fashion. However, the dark reality is that fast fashion has dire impacts on the environment and workers’ health, making it imperative for fashion designers to adopt ethical, eco-friendly methods of production.
Eco-friendly manufacturing is a process of manufacturing that protects the planet by conserving natural resources.
The transition to ethical manufacturers not only means better quality apparel but also better working conditions for factory laborers. Customers will be more willing to give you their brand loyalty and brand ambassadorship knowing that you treat your workers ethically and produce your apparel in safe working conditions.
The main purpose of transitioning to ethical and eco-friendly manufacturing is the ability to save our planet. Earth is only a mere half of a degree Celcius away from reaching the two-degree threshold of intense global warming. By choosing environmentally-conscious clothing fabrics, you are minimizing your brand’s carbon footprint and contributing less pollution, water, and energy waste.
Main problems in clothing manufacturing and how to avoid them
Problems in clothing manufacturing in any form can potentially affect the production performance, quality of garments, and timely delivery. While there is no such thing as the “seamless” process of clothing manufacturing, knowing these problems and dealing with them in the right manner is the solution.
Among those problems are communication issues, including failure to share Tech Pack changes, missing important information in the conversation thread, and a very common one - the language barrier.
Production planning and control are two of the most important aspects of the clothing manufacturing process. Precision in planning equates to on-time shipments of the appropriate supplies and their timely delivery to the factory. Production planning is a complex process and needs to be planned out way in advance, very often for the years ahead.
Production defects lead to wasted raw materials, extra manpower for sorting and eliminating issues, and unforeseen extra time. All of that lead to extra costs and lost money.
Let's just say production defects can happen even if both sides do their best. But there is a way to minimize production defects and deal with them quickly if they occur.
How to find clothing manufacturers for your business
One of the keys to fashion brand success is finding a right clothing manufacturer to work with. It has an impact on important business factors such as product cost and quality.

Here's our list of top clothing manufacturers currently managing clients with Techpacker
In order to find the right manufacturer for your business you will need to have some essentials on hand:
- Information about your product and brand goals.
- Determine what type of manufacturer you need.
- Have a time frame in mind.
- Determine how much you want to produce.
- Develop a tech pack.
- Have a working prototype or sample of your product on hand.
Online directories like Maker's Row and trade shows are the best places to look for a manufacturer. Thousands of manufacturers, suppliers, and wholesalers are listed in directories and are attending these shows to find new clients. There you can inquire about their development fees, yard/piece minimums, logistics, and payment terms. Learn our 5 tips on vetting clothing manufacturers.
Another important decision to make is to select a country for manufacturing. In the majority of sectors, Asia is the center of production. However, in recent years, there has been a resurgence of American-made products. Many fashion brands are eying Central and South America for faster production turnarounds. There has also been a significant increase in demand for South African clothing manufacturers.
Learn more about the global manufacturing trends here.
Bonus: how to start a clothing manufacturing business
Clothing manufacturing is a competitive market to emerge into. Finding the right segment is one of the keys to success. If you are planning to start an apparel manufacturing business important things to consider are:
- Main costs. Including brand design, license and permit fees, rent, marketing, and advertising costs, equipment, raw materials, staff wages, and salaries.
- Pricing strategy. Research what your competitors are charging and calculate your own cost per unit (CPU).
- Build a website and promote it online to start attracting customers.
- Choose your industry niche, decide what type of apparel you are going to produce. For example women, men's or kids' clothing.
- Plan your manufacturing process. What equipment you’ll need and if you need to recruit extra staff and whether special training will be required.
- Choose the right equipment for your manufacturing business.
Read a success story of a Singapore-based clothing manufacturer.
Thank you so much for reading! We hope this information was helpful for both designers and manufacturers. Stay tuned for more!